Structural correlates of heterogeneous in vivo activity of midbrain dopaminergic neurons.
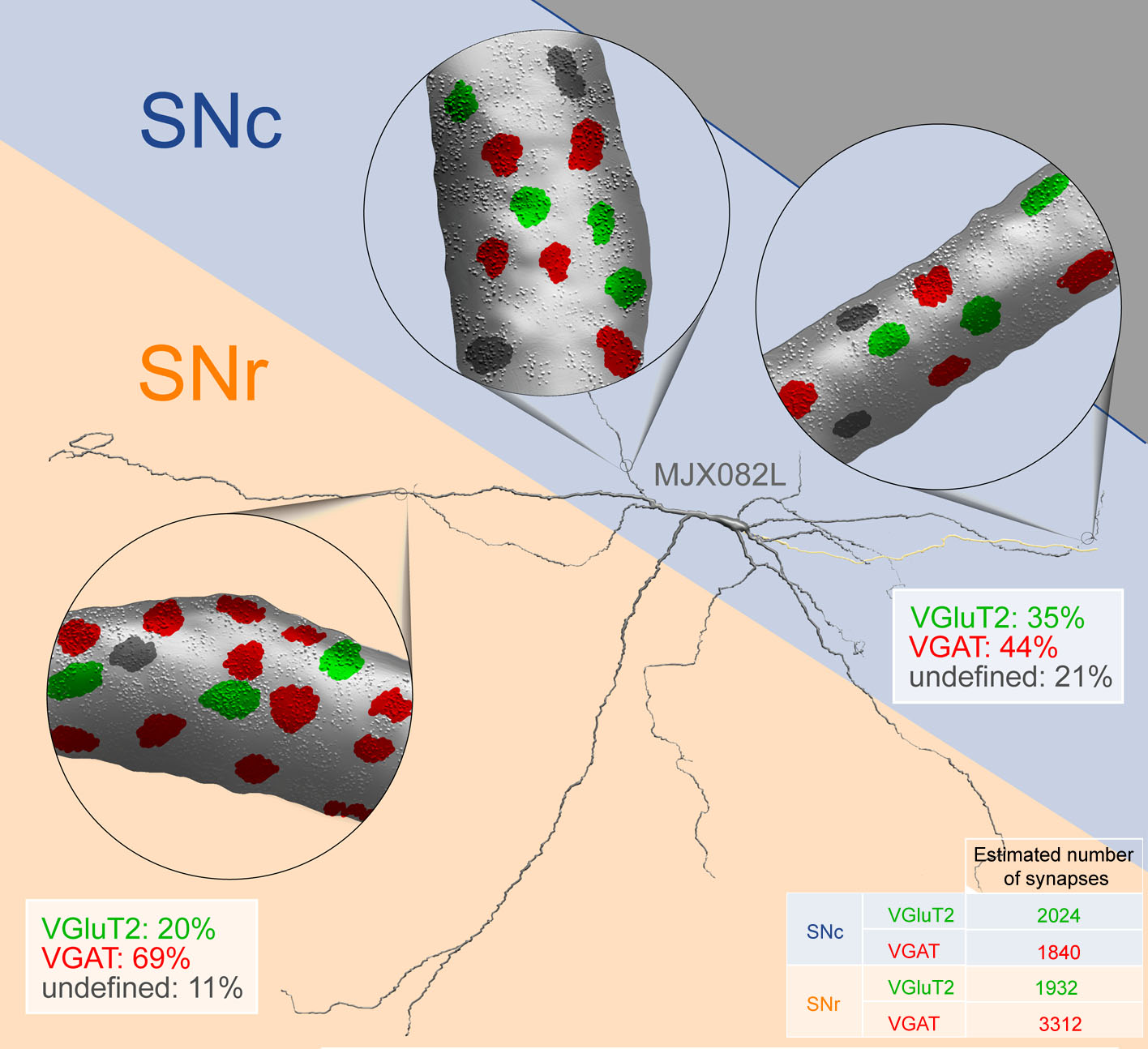
Dopaminergic neurons of the substantia nigra pars compacta (SNc) exhibit functional heterogeneity that likely underpins their diverse roles in behavior. We examined how the functional diversity of identified dopaminergic neurons in vivo correlates with differences in somato-dendritic architecture and afferent synaptic organization. Stereological analysis of individually recorded and labeled dopaminergic neurons of rat SNc revealed that they received approximately 8,000 synaptic inputs, at least 30% of which were glutamatergic and 40-70% were GABAergic. The latter synapses were proportionally greater in number and denser on dendrites located in the substantia nigra pars reticulata (SNr) than on those located in SNc, revealing the existence of two synaptically distinct and region-specific subcellular domains. We also found that the relative extension of SNc neuron dendrites into the SNr dictated overall GABAergic innervation and predicted inhibition responses to aversive stimuli. We conclude that diverse wiring patterns determine the heterogeneous activities of midbrain dopaminergic neurons in vivo.
2012.Nat. Neurosci., 15(4):613-9.
2024. Cell Rep, 43(4):114080.
2016.Curr. Biol., 26(7):916-20.