Directional local field potentials: A tool to optimize deep brain stimulation.
Electrical stimulation of the subthalamic nucleus, a small region of the brain that is important for controlling movement, can help treat some symptoms of Parkinson’s disease. Here, we show that the electrical waves generated by this brain region can be used to home in on the best site to stimulate for treatment.
BACKGROUND: Although recently introduced directional DBS leads provide control of the stimulation field, programing is time-consuming.
OBJECTIVES: Here, we validate local field potentials recorded from directional contacts as a predictor of the most efficient contacts for stimulation in patients with PD.
METHODS: Intraoperative local field potentials were recorded from directional contacts in the STN of 12 patients and beta activity compared with the results of the clinical contact review performed after 4 to 7 months.
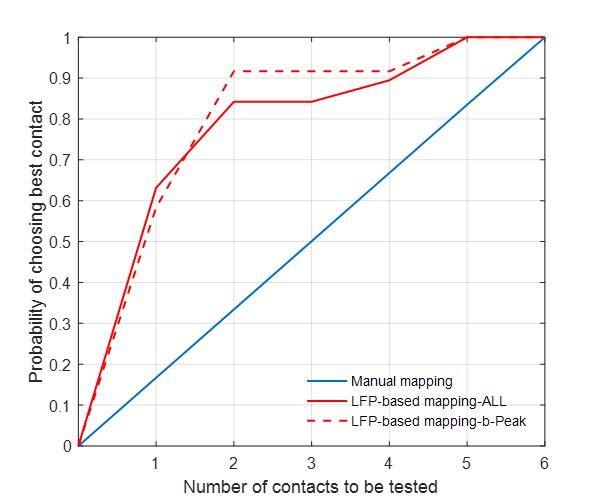
RESULTS: Normalized beta activity was positively correlated with the contact's clinical efficacy. The two contacts with the highest beta activity included the most efficient stimulation contact in up to 92% and that with the widest therapeutic window in 74% of cases.
CONCLUSION: Local field potentials predict the most efficient stimulation contacts and may provide a useful tool to expedite the selection of the optimal contact for directional DBS.
2023. Mov Disord, 38(5):818-830.
2022. NPJ Parkinsons Dis, 8(1):88.