Bilateral adaptive deep brain stimulation is effective in Parkinson's disease.
Continuous ‘deep brain stimulation’ is currently used as a treatment for Parkinson’s disease. We show in this paper that, by tailoring stimulation to those moments when it is needed, we can significantly improve the effectiveness of this treatment.
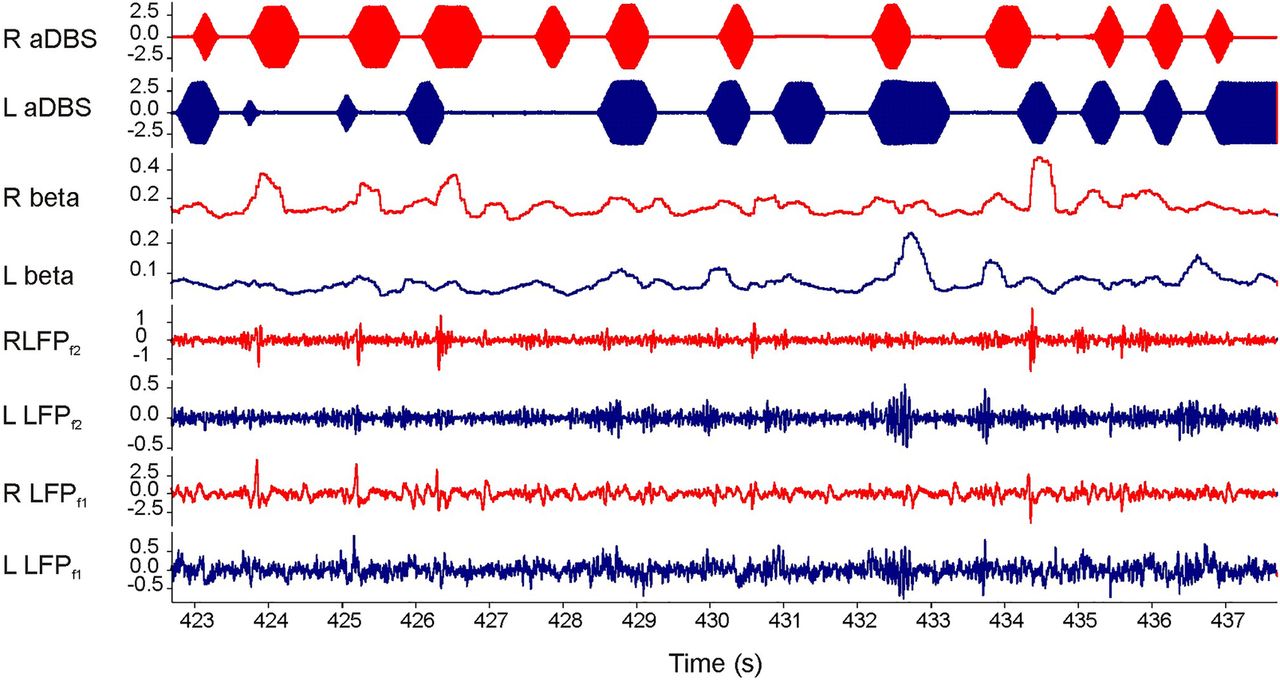
INTRODUCTION & OBJECTIVES: Adaptive deep brain stimulation (aDBS) uses feedback from brain signals to guide stimulation. A recent acute trial of unilateral aDBS showed that aDBS can lead to substantial improvements in contralateral hemibody Unified Parkinson's Disease Rating Scale (UPDRS) motor scores and may be superior to conventional continuous DBS in Parkinson's disease (PD). We test whether potential benefits are retained with bilateral aDBS and in the face of concurrent medication.
METHODS: We applied bilateral aDBS in 4 patients with PD undergoing DBS of the subthalamic nucleus. aDBS was delivered bilaterally with independent triggering of stimulation according to the amplitude of β activity at the corresponding electrode. Mean stimulation voltage was 3.0±0.1 volts. Motor assessments consisted of double-blinded video-taped motor UPDRS scores that included both limb and axial features.
RESULTS: UPDRS scores were 43% (p=0.04; Cohen's d=1.62) better with aDBS than without stimulation. Motor improvement with aDBS occurred despite an average time on stimulation (ToS) of only 45%. Levodopa was well tolerated during aDBS and led to further reductions in ToS.
CONCLUSION: Bilateral aDBS can improve both axial and limb symptoms and can track the need for stimulation across drug states.