Continuous Force Decoding from Deep Brain Local Field Potentials for Brain Computer Interfacing.
Brain computer interfaces enable people who cannot easily move or communicate to achieve these actions through computer-controlled devices. The patient controls these devices through their brain waves. Here, we demonstrate that electrical signals recorded from motor centres deep in the brain can be used to provide accurate and durable control.
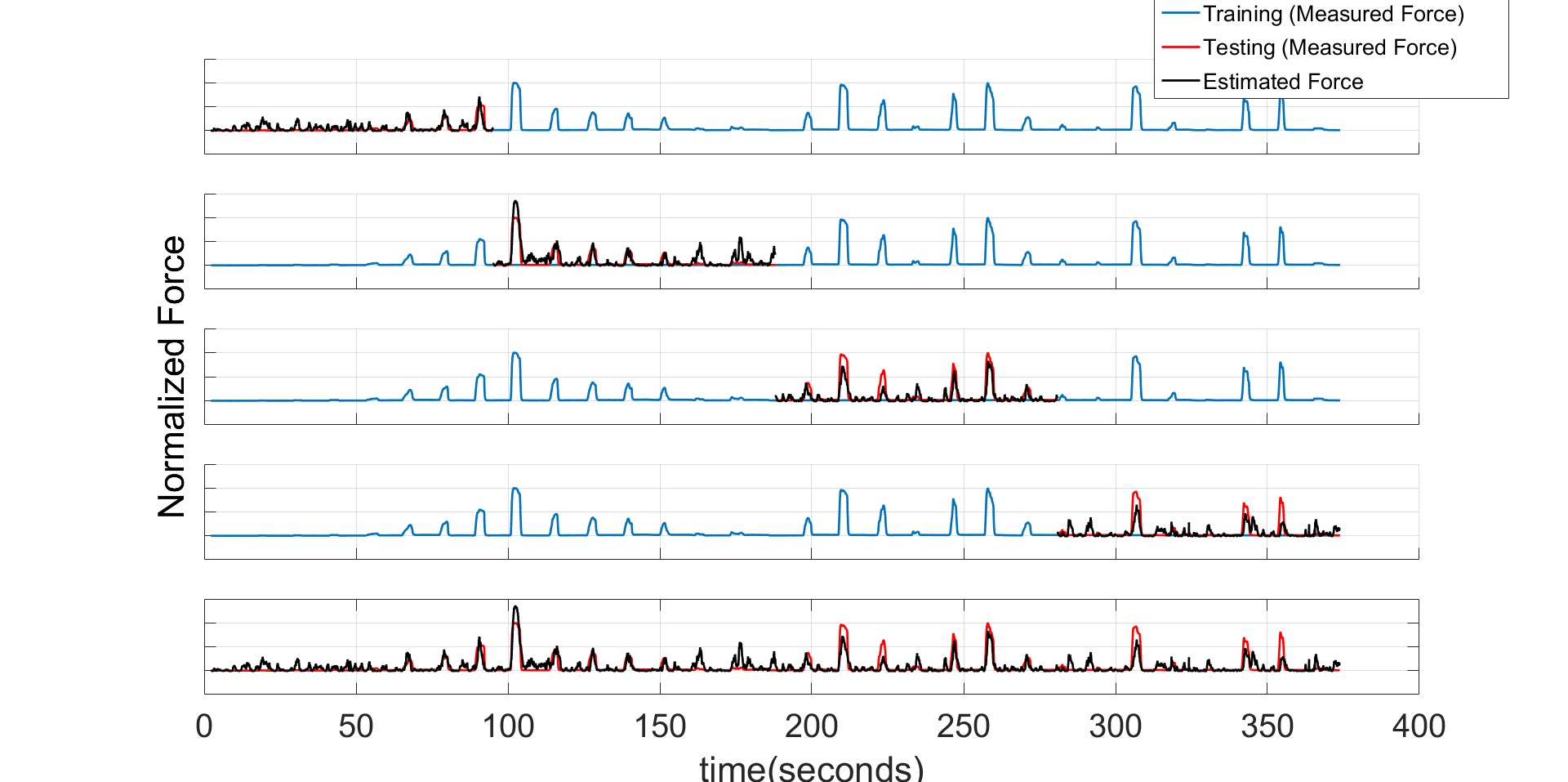
Current Brain Computer Interface (BCI) systems are limited by relying on neuronal spikes and decoding limited to kinematics only. For a BCI system to be practically useful, it should be able to decode brain information on a continuous basis with low latency. This study investigates if force can be decoded from local field potentials (LFP) recorded with deep brain electrodes located at the Subthalamic nucleus (STN) using data from 5 patients with Parkinson's disease, on a continuous basis with low latency. A Wiener-Cascade (WC) model based decoder was proposed using both time-domain and frequency-domain features. The results suggest that high gamma band (300-500Hz) activity, in addition to the beta (13-30Hz) and gamma band (55-90Hz) activity is the most informative for force prediction but combining all features led to better decoding performance. Furthermore, LFP signals preceding the force output by up to 1256 milliseconds were found to be predictive of the force output.
2017.Int IEEE EMBS Conf Neural Eng, 2017():371-374.