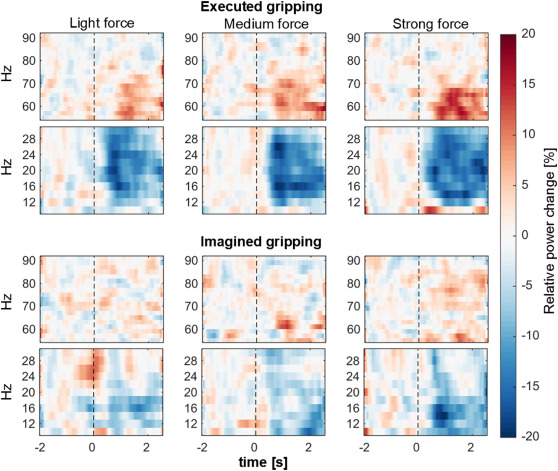
Subthalamic nucleus beta and gamma activity is modulated depending on the level of imagined grip force.
Some types of electrical activity recorded deep in the brain may be useful as ‘feedback’ signals that could help people affected by movement disorders to control their symptoms or prosthetic devices. However, for this feedback to be useful, similar brain signals must occur in the absence of voluntary movements. Here, we show that this is the case when people imagine movements of their hands.
Motor imagery involves cortical networks similar to those activated by real movements, but the extent to which the basal ganglia are recruited is not yet clear. Gamma and beta oscillations in the subthalamic nucleus (STN) vary with the effort of sustained muscle activity. We recorded local field potentials in Parkinson's disease patients and investigated if similar changes can be observed during imagined gripping at three different 'forces'. We found that beta activity decreased significantly only for imagined grips at the two stronger force levels. Additionally, gamma power significantly scaled with increasing imagined force. Thus, in combination, these two spectral features can provide information about the intended force of an imaginary grip even in the absence of sensory feedback. Modulations in the two frequency bands during imaginary movement may explain the rehabilitating benefit of motor imagery to improve motor performance. The results also suggest that STN LFPs may provide useful information for brain-machine interfaces.
2017.Int IEEE EMBS Conf Neural Eng, 2017():371-374.