The Effects of Theta-Gamma Peak Stimulation on Sensorimotor Learning During Speech Production
We used a non-invasive electrical brain stimulation and timed the input to brainwave patterns linked to learning. We applied it to the part of the brain that controls movements related to speech, to see if it could improve learning in speech tasks. Our main predictions weren’t supported, but follow-up analyses suggested it might help people retain speech learning longer.
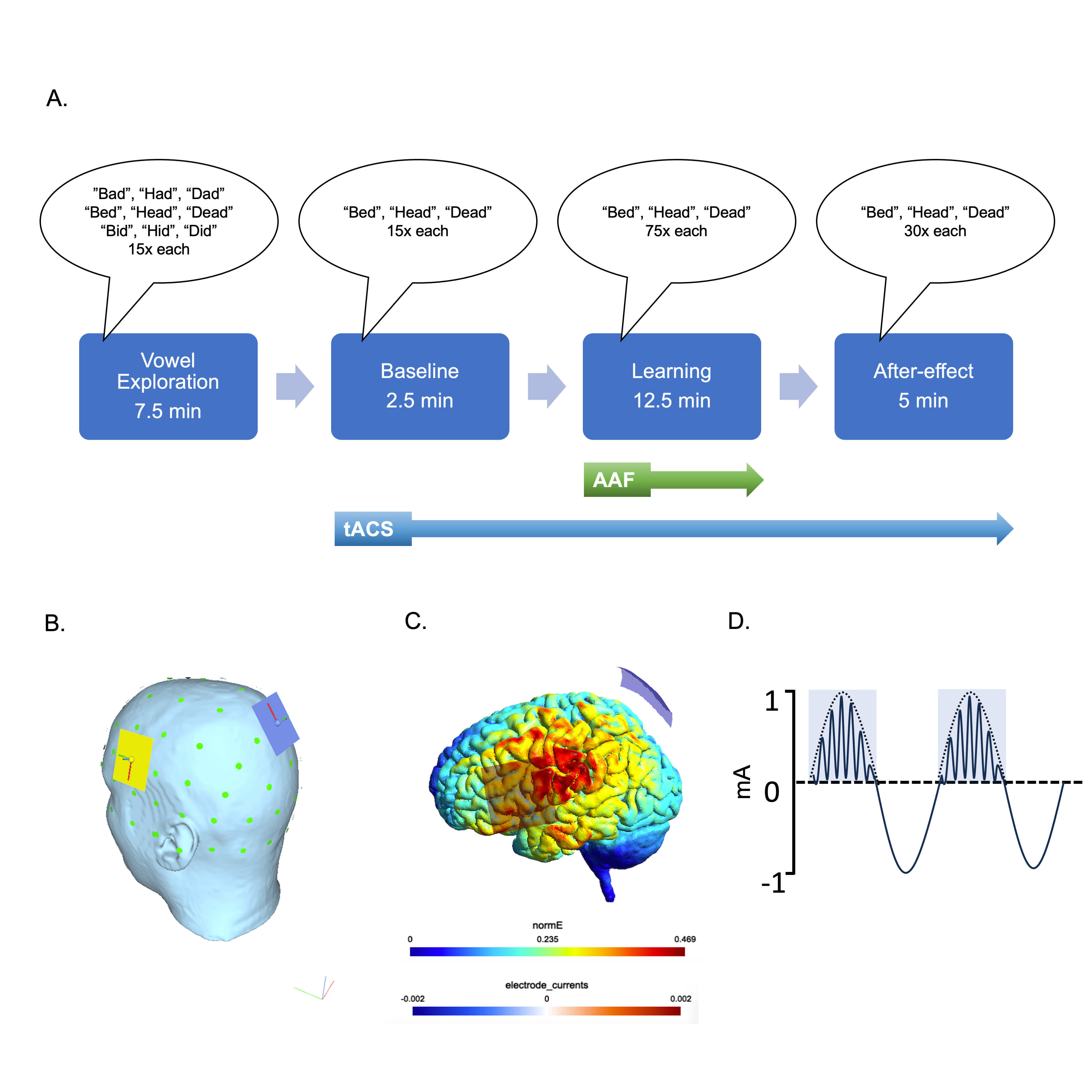
Abstract Transcranial alternating current stimulation (tACS) is a noninvasive neuromodulatory tool that is thought to entrain intrinsic neural oscillations by supplying low electric currents over the scalp. Recent work has demonstrated the efficacy of theta-gamma phase-amplitude coupled tACS over primary motor cortex to enhance motor skill acquisition and motor recovery after stroke. Here, we wished to assess the efficacy of tACS delivered with 75-Hz gamma coupled to the peak of a 6-Hz theta envelope (theta-gamma peak; TGP) at an intensity of 2 mA peak-to-peak to enhance sensorimotor learning during speech production. Sensorimotor learning was measured by shifting the formant frequency of vowels in real-time as speech is produced and measuring the adaptation to this altered feedback. The study was a between-subjects, single-blind, sham-controlled design. We hypothesised that participants who performed the speech task while receiving TGP tACS over the speech motor cortex (N = 30) would show greater adaptation to altered auditory feedback than those receiving sham stimulation (N = 31). Contrary to this hypothesis, there was no effect of TGP tACS on adaptation to the upwards F1 shift in auditory feedback in either the final 30 trials of the learning phase or in the first 15 trials of the after-effect phase. However, a trend emerged in the TGP tACS group for greater retention of the adapted state and slower return to baseline F1 values in the after-effect phase. This finding was not predicted, and highlights the need for further investigation to deepen our understanding of the effects of TGP tACS on speech motor learning.
2021. eLife, 10:e67355
2024. Brain Stimul, 17(2):392-394.
2022. Brain Stimul, 15(6):1513-1516.