Prototypic and arkypallidal neurons in the dopamine-intact external globus pallidus.
The external pallidum is a brain region important for movement. Past work has shown that the pallidum in a model of Parkinson’s disease contains two main types of nerve cell. Here, we show that these two cell types also exist in the healthy brain. They have different molecular building blocks, connections and electrical activity, allowing them to perform a ‘division of labor’ to control behaviour.
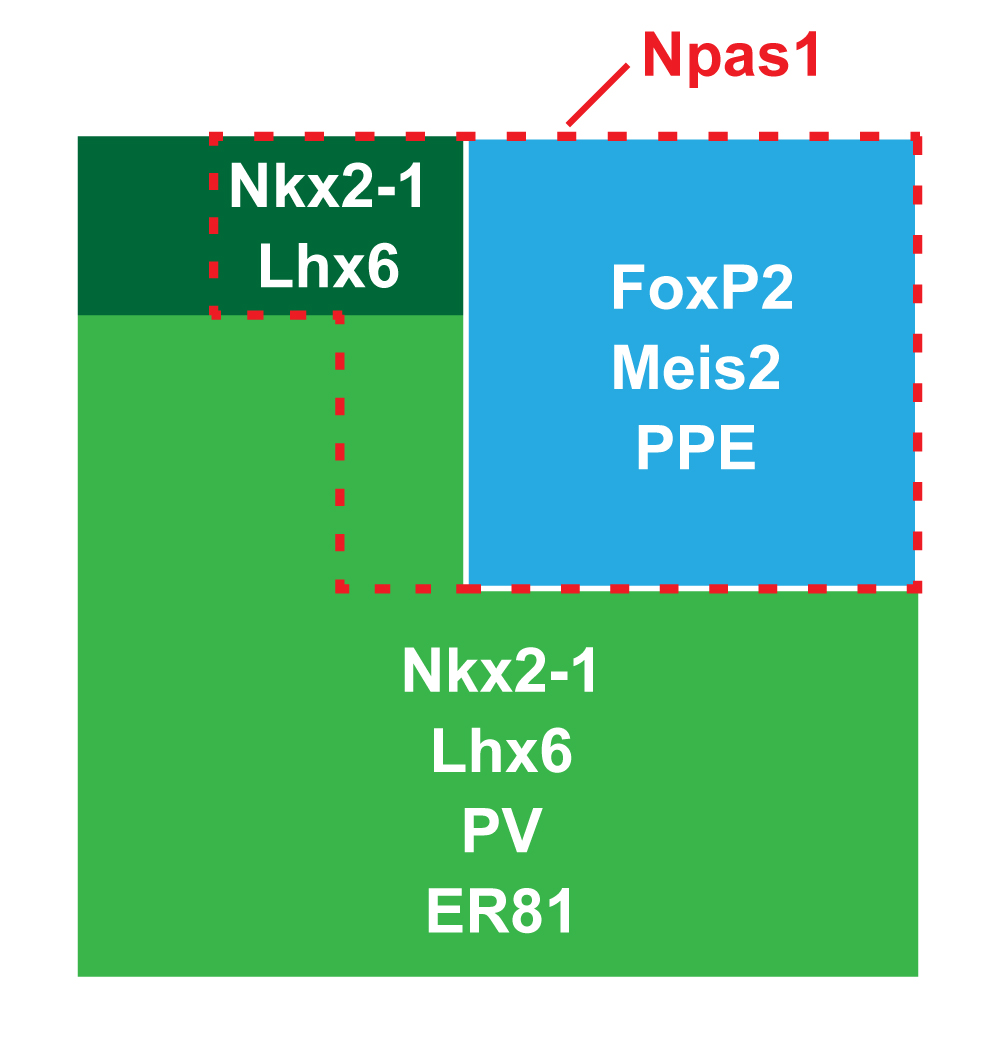
Studies in dopamine-depleted rats indicate that the external globus pallidus (GPe) contains two main types of GABAergic projection cell; so-called "prototypic" and "arkypallidal" neurons. Here, we used correlative anatomical and electrophysiological approaches in rats to determine whether and how this dichotomous organization applies to the dopamine-intact GPe. Prototypic neurons coexpressed the transcription factors Nkx2-1 and Lhx6, comprised approximately two-thirds of all GPe neurons, and were the major GPe cell type innervating the subthalamic nucleus (STN). In contrast, arkypallidal neurons expressed the transcription factor FoxP2, constituted just over one-fourth of GPe neurons, and innervated the striatum but not STN. In anesthetized dopamine-intact rats, molecularly identified prototypic neurons fired at relatively high rates and with high regularity, regardless of brain state (slow-wave activity or spontaneous activation). On average, arkypallidal neurons fired at lower rates and regularities than prototypic neurons, and the two cell types could be further distinguished by the temporal coupling of their firing to ongoing cortical oscillations. Complementing the activity differences observed in vivo, the autonomous firing of identified arkypallidal neurons in vitro was slower and more variable than that of prototypic neurons, which tallied with arkypallidal neurons displaying lower amplitudes of a "persistent" sodium current important for such pacemaking. Arkypallidal neurons also exhibited weaker driven and rebound firing compared with prototypic neurons. In conclusion, our data support the concept that a dichotomous functional organization, as actioned by arkypallidal and prototypic neurons with specialized molecular, structural, and physiological properties, is fundamental to the operations of the dopamine-intact GPe.